Since the 1980s, when Motorola first made famous the quality improvement methodology, Six Sigma has received much recognition and praise as companies have implemented it to improve their bottom line.
When looking at a list of companies who have implemented Six Sigma with great results – companies like General Motors, Ford Motor Co., Kodak, Boeing, 3M, Dell, and GE – it’s easy to understand why some industry professionals assume Six Sigma is only for manufacturers. But the methodology can be used effectively in service industries as well, such as healthcare, education and financial services, with equal results.
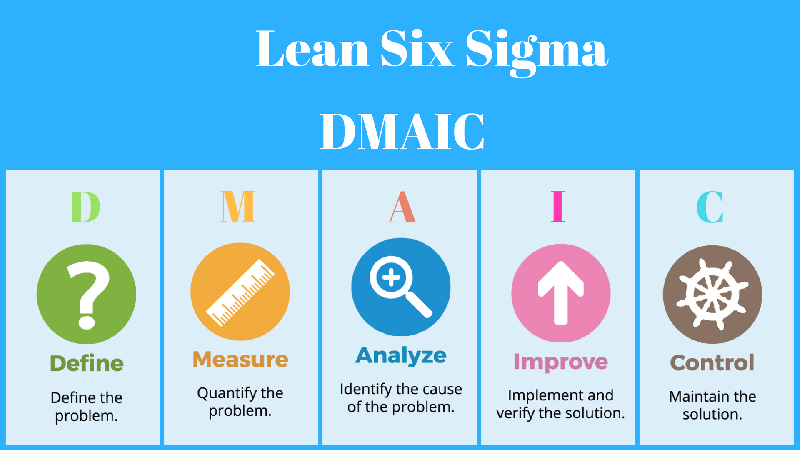
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a business improvement methodology that aims to maximize shareholders’ value by improving quality, speed, customer satisfaction, and costs. It achieves this by merging tools and principles from both Lean and Six Sigma. It has been widely adopted widely in manufacturing and service industries, and its success in some famous organizations (e.g. GE and Motorola) has created a copycat phenomenon, with many organizations across the world willing to replicate the success.
Lean and Six Sigma have followed independent paths since the 1980s, when the terms were
first hard-coded and defined. The first applications of Lean were recorded in the Michigan
plants of Ford in 1913, and were then developed to perfection in Japan (within the Toyota
Production System), while Six Sigma saw the light in the United States (within the Motorola
Research Centre).
Lean is a process-improvement methodology, used to deliver products and services better,
faster, and at a lower cost. Womack and Jones (1996) defined it as:… a way to specify value, line up value-creating actions in the best sequence, conduct those activities without interruption whenever someone requests them, and perform them more and more effectively. In short, lean thinking is lean because it provides a way to do more and more with less and less—less human effort, less human equipment, less time, and less space—while coming closer and closer to providing customers with exactly what they want.

Six Sigma is a data-driven process improvement methodology used to achieve stable and predictable process results, reducing process variation and defects. Snee (1999) defined it as: ‘a business strategy that seeks to identify and eliminate causes of errors or defects or failures in business processes by focusing on outputs that are critical to customers’.
While both Lean and Six Sigma have been used for many years, they were not integrated until the late 1990s and early 2000s (George, 2002; George, 2003). Today, Lean Six Sigma is recognized as: ‘a business strategy and methodology that increases process performance resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction and improved bottom line results’ (Snee, 2010).
Lean Six Sigma uses tools from both toolboxes, in order to get the best from the two
methodologies, increasing speed while also increasing accuracy.
The benefits of Lean Six Sigma in the industrial world (both in manufacturing and services)
have been highlighted extensively in the literature and include the following:
1. Ensuring services/products conform to what the customer needs (‘voice of the
customer’).
2. Removing non-value adding steps (waste) in critical business processes.
3. Reducing the cost of poor quality.
4. Reducing the incidence of defective products/transactions.
5. Shortening the cycle time.
6. Delivering the correct product/service at the right time in the right place. (Antony,
2005a; Antony, 2005b)
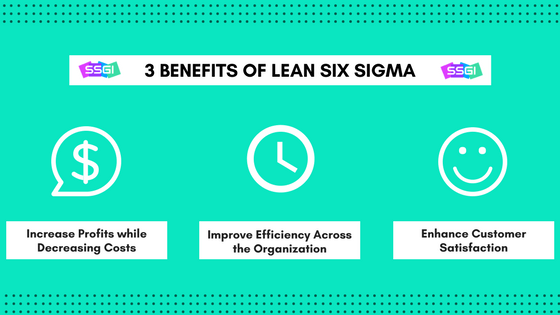
However, to make Six Sigma implementation successful in the service industry,
managers must shift their focus from thinking about numbers to thinking about aligning processes to business needs. Applying the right kind of metrics to bring about an improved business performance is very essential. Before implementing a significant Six Sigma implementation within your organization, you must prove to your people its benefits so that they ultimately give in to accept the change enthusiastically.
Six Sigma helps in improving on lots of processes like generating business expansion, improving customer service, and gaining knowledge about service sectors business processes. Six Sigma also helps to improve the processes involved with human resources, marketing, and sales. Using the DMAIC (Define – Measure – Analyze – Improve – Control) methodology, Six Sigma helps in implementing quality in any industry by reducing defects. The defects are first identified, data is collected as to how the defects occur, and then a new method of working is implemented to reduce errors in the future. This methodology has helped various financial sectors, insurance companies, educational institutes, management companies, state agencies, and high-tech companies to improve their quality.
Three principles of statistical thinking are required to be applied across service industries, which are namely – all work is a process, all processes have variability, and all processes create data that explains variability. Using the DMAIC model, aimed at reducing defects, the first step is to figure out the defects. The next step involves collecting data to find out why and how the defects occur. After the data is measured, a standard process is analyzed and announced to be used across the industry for improvement. And lastly, the improvement in customer satisfaction and increased business is maintained with those standard processes.
SOURCE:



0 Comments